Due to the strong regional and diurnal variation of rainfall, accurate measurement of rainfall has been difficult to achieve in history. After the establishment of the modern Western scientific observation system, many famous scientists including Franklin began to conduct in-depth research on automated quantitative measurement of rainfall. As a result, rain gauges with different forms or principles have appeared in the history of different countries. Scientists found that the accuracy of rain gauge measurement is closely related to its material, opening size, height of the opening from the ground, and the surrounding environment. Today, most rain sensors are made of plastic that is not easily damaged and more durable.
What is a rain gauge?
A rain gauge is an instrument used to measure the amount of precipitation in a certain area over a period of time (the measurement of snowfall requires the use of a snow gauge). There are many types. Most rain gauges use millimeters as the unit of measurement, and sometimes the measurement results are in inches or centimeters as the unit. The reading of the rain gauge can be read manually or using an automatic weather station, and the frequency of observation can be changed according to the requirements of the collecting unit. In most cases, the collected rainwater will no longer be retained after observation, but there are also a few weather stations that will retain it as a sample for pollution level or other tests.
How does a rain gauge work?
The rain gauge working principle is actually very simple. The one in the picture below, like the seesaw model, is the rainfall gauge unit of measurement. This instrument will be connected to an electronic recorder. When the rainfall on it reaches a certain value, the weight of the rain will cause the seesaw to jump. One-click, whenever it beats, the electronic recorder will record a piece of data, how many points are totaled and how many pieces of data are transmitted to the computer, and then use the computer to calculate the overall data to form a statistical graph and a data graph, which is then formed into rainfall.
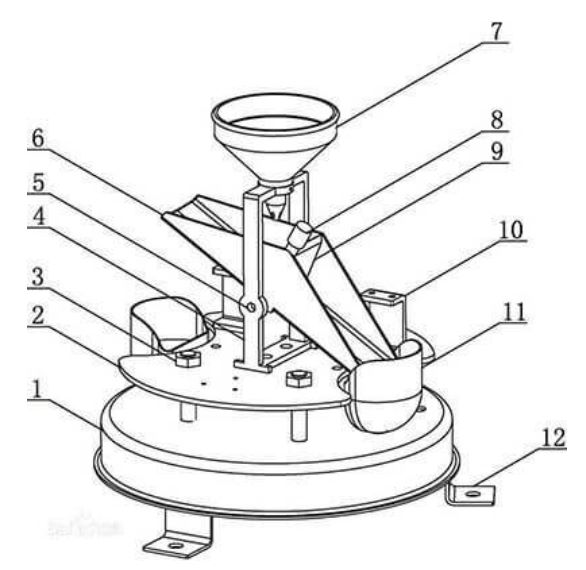
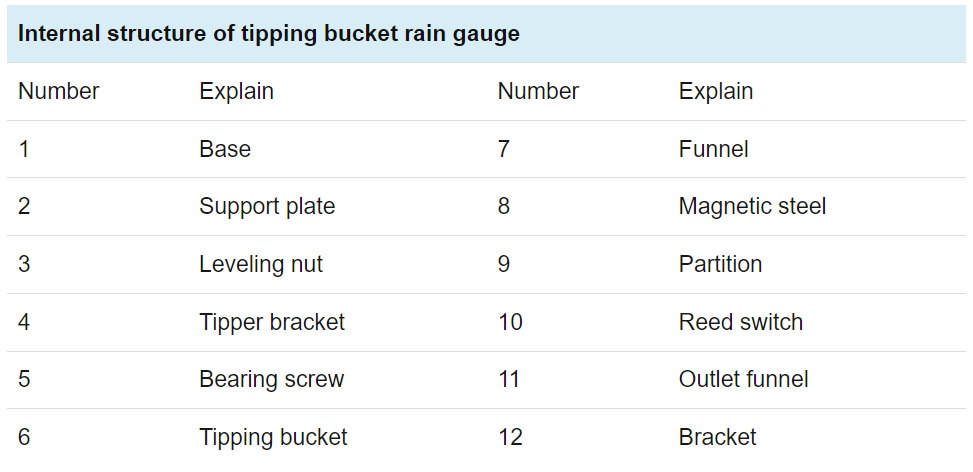
What is a rain gauge used for?
In terms of meteorology, the rain gauges can record the size of the current rainfall in time, which is very practical. The tipping bucket rain gauges in the rain gauges is a wired telemetry instrument that can continuously record the precipitation over time and measure the accumulated precipitation. It is divided into two parts: a sensor and a recorder, which are connected by a cable.
The siphon rain gauges are instrument that can continuously record precipitation and precipitation time. The shape and size of the upper water funnel are the same as the rain gauges. The standard rain gauges are instrument used to measure the accumulated precipitation over a period of time. The shell of the common standard rain gauges are transparent glass or plastic. For the area and shape of the container mouth, a water storage bottle is placed in the lower tube to collect rainwater.
According to the difference in appearance and
principle, this article mainly introduces three types of rain gauges. They are:
Let’s introduce in detail the work, reading, and maintenance of each type.
Standard rain gauges
The standard rain gauges are currently a widely used and inexpensive rain gauges. Just fix it in an open area that needs to receive rainwater to work. The standard rain gauges working principle is to collect falling rainwater in a funnel-shaped collector connected to a measuring tube. The diameter of the collector is 10 times the diameter of the tube. Therefore, the working principle of the rainfall gauge is to magnify the liquid by 10 times.
Magnifying rainwater in this way can be accurately measured to one-hundredth of an inch. The amount exceeding the capacity of the tube is clamped in the housing of the meter, allowing the recorder to pour out the liquid in the tube and fill it up when needed.

How to read standard rain gauge?
Recording rainfall using a standard or funnel rainfall gauge is usually done manually. It is important to be as accurate as possible when reading the meter. When taking the reading, the rain gauges must be kept level, and your line of sight must be flush with the water surface in the instrument, and read the lowest point of the sunken water surface. The reading should be accurate to one decimal place.
If the amount of precipitation is large and the amount cannot be completed at one time, it can be divided into multiple amounts. After each measurement, it shall be recorded and the total amount of precipitation shall be accumulated. In the event of solid precipitation such as ice and snow, the funnel should be replaced with a snow-bearing port, so that the solid precipitation can directly fall into the rain gauge (the water storage bottle should be covered to prevent evaporation), and it should be placed in a warm place or added Quantitative warm water (boiling water cannot be used or too much added). After the ice and snow are melted, measure with a measuring cup, and then subtract the added warm water from the measured result to get the measured solid precipitation.
Standard rain gauges installation
Place the standard rain gauges on a fixed shelf in the observation area. The mouth of the organ is kept level, 70 cm above the ground. In areas with deep snow in winter, a backup shelf that can make the height of the rain gauge reach 1.0-1.2 meters from the ground should be installed nearby. When the snow depth exceeds 30 cm, the instrument should be moved to the backup shelf for observation.
When it snows in winter, the funnel must be unscrewed from the mouth of the device (for stations with old rain gauges, the snow bearing mouth must be replaced), the water storage bottle shall be taken away, and the snow bearing mouth and water storage tank shall be used directly to hold the precipitation.
How to clean rain gauges?
After the precipitation stops in the warm
season, supplementary observations should be made immediately to avoid excessive
evaporation and incorrect precipitation measurement.
The measuring cylinder and water storage bottle
of the rain gauge should be kept clean frequently and should be cleaned and
inspected at least once a month.
Don’t check the cylinder for leaks in winter
or rainstorm season.
Every time you check the equipment and
equipment, you should pay attention to whether there is any blockage in the
water holder and the water funnel, and whether there is any debris such as
sharp soil, leaves, etc. in the water cylinder. If there is any debris, it
should be removed immediately.
Tipping bucket rain gauges
The tipping bucket rain gauge is one of the
weather sensors. Compared with the standard rain gauge, its measuring elements
are more complicated and the data is more accurate. It can be used as an
outdoor rain gauge alone, or it can be used with an outdoor weather station.
Its biggest advantage is that it does not require manual readings and avoids
manual errors.
How a tipping bucket rain gauges work? The
tipping bucket rain gauge is a typical weather station rain gauges. It is most
accurate rain gauges. The tipping bucket rain gauges working principle uses the
tipping bucket principle to monitor rainfall changes in real-time. The tipping
bucket rainfall sensor is a mechanical bistable structure. Due to gravity, it
overturns and is in a waiting state. This process will generate a pulse signal
to be recorded and reported to the cloud server through wireless communication
to provide data support for industry users’ command and decision-making and
improve hydrological monitoring capabilities. At present, the materials of
tipping bucket rain gauge commonly used in the market are professional
stainless steel rain gauges and cheap ABS rain gauges.

Tipping bucket rain gauges reading
Installation and commissioning
1.The installation height of the rainfall sensor
is 0.7m (the distance from the plane of the bearing aperture to the ground of
the observation site) for the continuity and comparability of the observation
data in this area. The height of 1.2m can also be used in the northern area.
2.When the rain sensor is installed, use a level
to level the rain-bearing mouth.
3.The installation holes of the three feet on
the base of the rain sensor are fixed on the concrete base with three M8 anchor
bolts and spirals (or expansion screws). The depth of the base buried in the
soil should be able to ensure that the instrument is installed firmly and will
not shake or tilt in a storm.
Note: When pouring the foundation concrete, it
should be ensured that the three anchor bolts are divided into 120 equal parts.
4.Adjust the leveling screw to center the round
bubble. After the instrument is leveled, slowly tighten the three fixing
screws. If the level bubble changes, readjust it again. Hold it firmly.
5.The base should have drainage pipe outlets and
cable channels. If it is necessary to collect the drainage volume to test the
measurement accuracy of the system, a small room (pit) for the collection
container should be constructed.
6.The signal output cable is a two-core shielded
cable (A43VVT2*16/0.15 microphone cable).
7.The cable is inserted through the rubber cable
sheath of the instrument base and locked with a screw cap to increase the
tensile strength and prevent the wiring from pulling off. The two-core wires of
the cable are stripped 20mm in length, folded in half, twisted into strands,
inserted into the two wiring holes of the commonly used signal-transmitting
parts in the terminal block, and fastened with screws.
8.Gently dial the parts of the tipping bucket
with your hand to check whether the signal of the receiving part is normal.
9.Perform manual water supply verification.
10.Put the rain receiver components on the base
of the instrument. At this point, the instrument is installed.
Maintenance of rain gauges
1. Pay attention to protect the instrument from
collisions, especially the mouth of the device must not be deformed; ensure
that the body is stable and the mouth of the device is level. Vernier calipers
and spirit levels can be used for inspection every year. For unmanned rain
gauge stations, special safety protection measures should be taken for the
instruments.
2. During the use of the instrument, the silt
(silt, dust, leaves, insects, and other debris) should be regularly dredged
according to the actual local conditions, the water channels should be checked
and dredged, and the ring and inner surface of the rain receiver should be
wiped to ensure unblocked water flow.
3. If there is mud and sand in the water chamber
of the tipping bucket, it can be cleaned with clean water or alcohol with a
cleaning pen. Do not touch the inner wall of the bucket with fingers to prevent
oil stains and affect the measurement accuracy of the tipping bucket.
4. If there is a sense of blocking during the
turning of the tipping bucket components, clean water or alcohol to clean the
shaft journals at both ends of the tipping bucket shaft and the holes of the
jewel bearing, especially in windy and sandy stations. If the cleaning is not
effective, it may be caused by long-term use of the bearing sleeve and wear or
breakage of the jewel bearing. Use a pin to touch the surface of the inner hole
of the bearing. If there is a sense of blockage, the jewel is worn or broken,
and the bearing parts should be replaced. If the bucket shaft is damaged, the
bucket shaft should be replaced.
5. Do not add oil to the jewel bearing to avoid
dust collection, due to dust (contains alumina and carbonized components)
The hardness is very high, and the grinding
force is extremely strong, just like an abrasive, it can wear the bearing
surface, increase the friction torque, and cause premature damage.
6. The axial working clearance of the support
shaft of the tipping bucket component should be checked frequently, too large
or too small will affect the normal operation of the tipping bucket component.
When replacing the jewel bearing or the tipping bucket shaft, the axial working
clearance of the tipping bucket shaft should be carefully adjusted. Because of
the high hardness and brittleness of the jewel bearing, the journal area of
the dump shaft is small and the pressure per unit area is very large. If the
interference is large, the jewel bearing is easily damaged if the assembly is
not careful.
7. Do not twist the fine-tuning nails for
adjusting the inclination of the tipping bucket components (measuring the
amount of water) at will. At the same time, pay close attention to making it
loose; the round blister should be placed in the center. The correctness of the
two parts of the work is the basis of the measurement accuracy of the
instrument.
8. When the instrument is placed indoors or
working in the field, it is believed that when there is no rain, dust will fall
into the rain receiver, and the mouth of the device can be tightly covered with
a tube cover.
Like the tipping bucket rain gauges, the optical rain gauge is also an automatic rain gauge, relying on built-in sensors and other accessories to automatically count rainfall, and upload the data to the cloud platform through wired or wireless means for customers to view.

Optical rain gauges working principle
The optical rain gauge is a new type of
meteorological rain gauge, based on the principle of photoelectric detection,
mainly used to measure rainfall. The principle of infrared light sensing is
used to judge the amount of rainfall by using the characteristic of different
light transmission properties when there are water droplets in the air.
Multiple optical probes are built in, and the light path is strictly analyzed.
When raindrops pass through the sampling space, the raindrops will block the
laser, and the light signal received by the receiving sensor and the electrical
signal converted from the light signal will change. When the raindrops pass
through the sampling space, the electrical signal from the receiving sensor
will resume and enter the sampling space. The previous state. When the
raindrops traverse the sampling space, the electrical signals of the receiving
sensor are processed, and the time for the raindrops to traverse the sampling
space can be obtained.
Optical rain gauges installation
The rain sensor needs to be installed in an open
place, and there should be no obstructions around and above it. Install the
device on the bracket in the accessories first, and fix the device and the
bracket with 4 M4*35 304 stainless steel screws and nuts. Then install the
bracket to the position to be installed (the position to be installed needs to
be opened with a φ5 round hole), the bracket should be installed horizontally,
and finally the tray and the equipment are fixed by three M4*10 304 stainless
steel screws and nuts.
Optical rain gauges maintenance
The rain gauge needs to be outdoors for a long
time, and the use environment is very harsh. Therefore, the surface of the
instrument should be kept clean and often wiped with a soft cloth. The
instrument should be cleaned once a month for long-term operation and once
every three months.
Conclusion
In the study of meteorological elements,
rainfall is an important part of it. Measuring rainfall is of great
significance to people’s production and life. For example, whether rainfall can
meet the growth of crops in a certain period of time, how to determine the
climate conditions and weather forecasts of a certain area. Before the Internet
of Things technology was popularized, the monitoring and management of regional
rainfall was relatively simple, basically relying on manual reading of data.
During periods of heavy rainfall, it is difficult to obtain the latest
real-time water level information.
Therefore, it is very important to choose the right measuring tools and measuring methods. Standard rain gauges are loved by meteorological enthusiasts and rainfall researchers. Tipping bucket rain gauges are often used with weather stations. The best place for the automatic rain gauge is outdoor. Optical rain gauges are of great significance to aviation and navigation.

