1. Introduction
As an important member of the sensor family, pressure sensors are used in many fields such as industry, medical care, and automobiles, playing an irreplaceable role.
2. Introduction to Pressure Knowledge
Pressure is a basic concept in physics, which refers to the ratio of the force acting vertically on the surface of an object to its contact area. In daily life, we feel the existence of pressure all the time, whether it is atmospheric pressure, water pressure, or contact pressure between mechanical parts, all of which are "used" by pressure sensors.
The Torricelli experiment that we are familiar with in high school physics tests atmospheric pressure.


In 1648, French scientist Pascal heard about Torricelli's experiment and Galileo's experiment, and devoted himself to studying the reasons for the results. Finally, he concluded that the height of the mercury column falling is equal to the mass of the air. He used a formula to explain this force, which he called "pressure". Later, in order to commemorate his contribution to the study of pressure, the unit of pressure was defined as "Pascal".
Let's take a look at the commonly used units of pressure:

The international standard unit uses Pascal (Pa) to measure pressure, where one atmosphere (ATM) corresponds to 105Pa. As the altitude rises, the atmospheric pressure gradually decreases, and this feature allows some pressure gauges to be used to measure altitude. When the aircraft climbs to an altitude of 10,000 meters, the air pressure will be about 30% lower than that at sea level. Therefore, in order to ensure the comfort of passengers, the air pressure inside the aircraft must be increased. During the descent of the aircraft, due to the change in air pressure difference, passengers may feel the discomfort of tinnitus.
In the United Kingdom and the United States, people are accustomed to using PSI (pounds per square inch) or inH2O (inches of water column) as the unit of measurement for pressure.
Here, we need to clarify the concept of "force": force refers to the force acting vertically on a point on the surface of an object. Its units of measurement include kilograms (Kg) and Newtons (N). For example, weighing, thrust, torque, etc., all belong to the measurement scope of force/torque sensors, and we will explain them in detail in subsequent content.
3. Measurement principle of pressure sensor
The working principles of pressure sensors vary, but in the final analysis, they all convert the physical quantity of pressure into electrical signals for transmission and processing.
There are many types of pressure sensors, such as piezoresistive pressure sensors, piezoelectric pressure sensors, resistive strain pressure sensors, inductive pressure sensors, capacitive pressure sensors, resonant pressure sensors, thin film pressure sensors, etc.
Currently, the most widely used pressure sensors are: diffused silicon piezoresistive (MEMS) pressure sensors, ceramic piezoresistive pressure sensors, ceramic capacitive pressure sensors, strain pressure sensors, sputtered thin film pressure sensors, and high temperature resistant sapphire pressure sensors.
4. Classification of pressure sensors
According to the type of measurement, pressure sensors can be divided into:
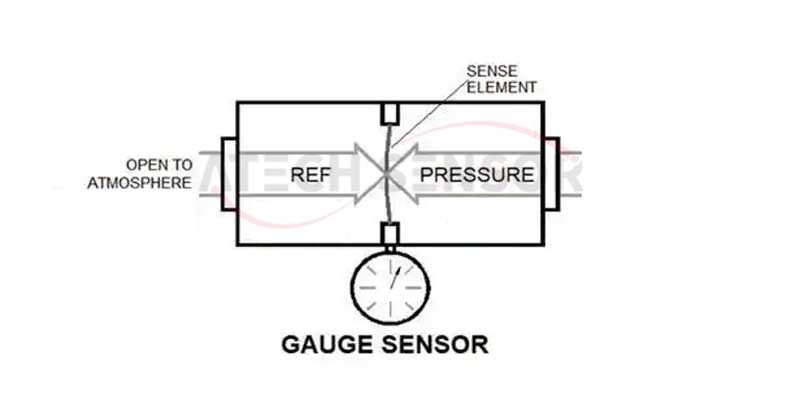
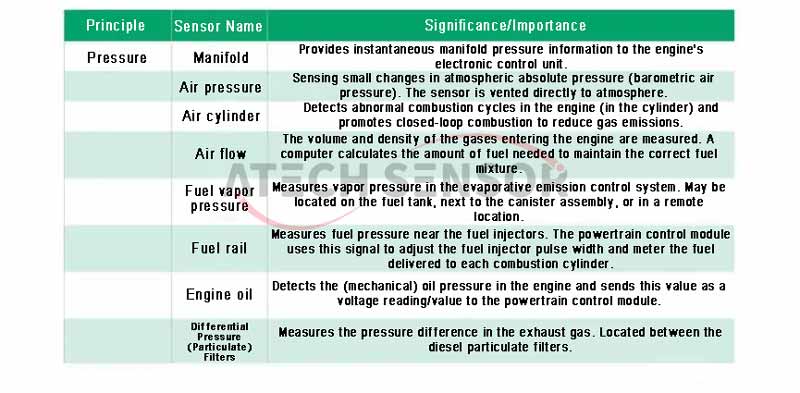
1) Gauge pressure sensor: used to measure the pressure of the medium relative to atmospheric pressure. The measured pressure corresponds to atmospheric pressure, which is expressed in English as G (Gauge).
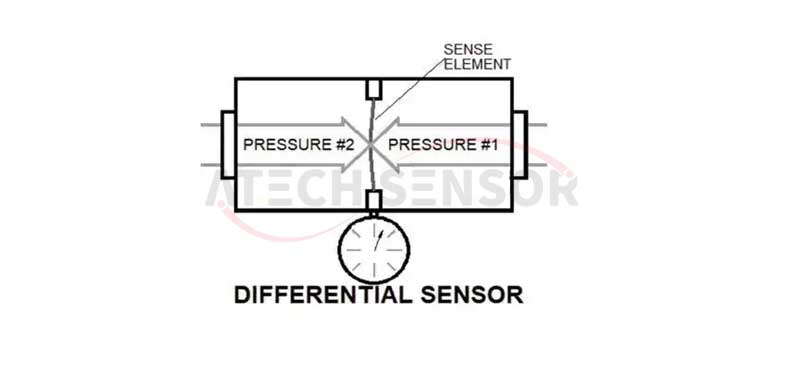
2) Differential pressure sensor: used to measure the pressure difference between two different media. The differential pressure sensor mainly measures the difference between two pressures, which is expressed in English as D (Differential).
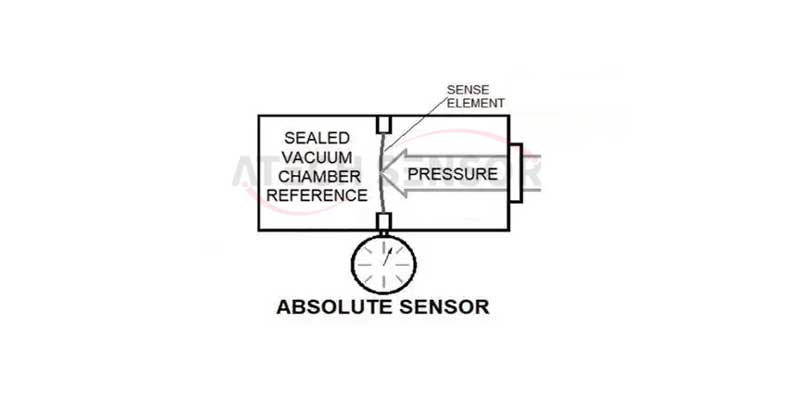
3) Sealed pressure sensor: used to measure the pressure of the medium relative to a certain sealing pressure. The sealing pressure can be selected by yourself when the sensor is produced. The English expression is S (Sealed).
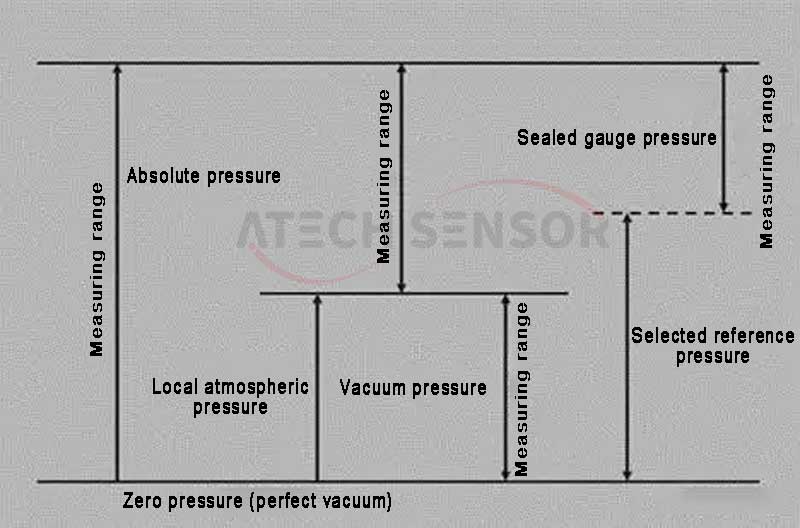
4) Compound pressure sensor: measures negative gauge pressure and positive gauge pressure. Compound pressure sensor provides a linear output signal from full vacuum to zero pressure to full scale pressure. It is represented by C (compound) in English. The figure shows a reference differential pressure sensor.
5. Typical applications of pressure sensors
Pressure sensors play an important role in many industries due to their wide range of applications and unique measurement capabilities. The following are some typical application scenarios:
1) Industrial field: In the industrial manufacturing process, pressure sensors are widely used in fluid pressure monitoring, equipment operation status monitoring, production process control and other links, providing strong support for the automation and intelligence of industrial production.
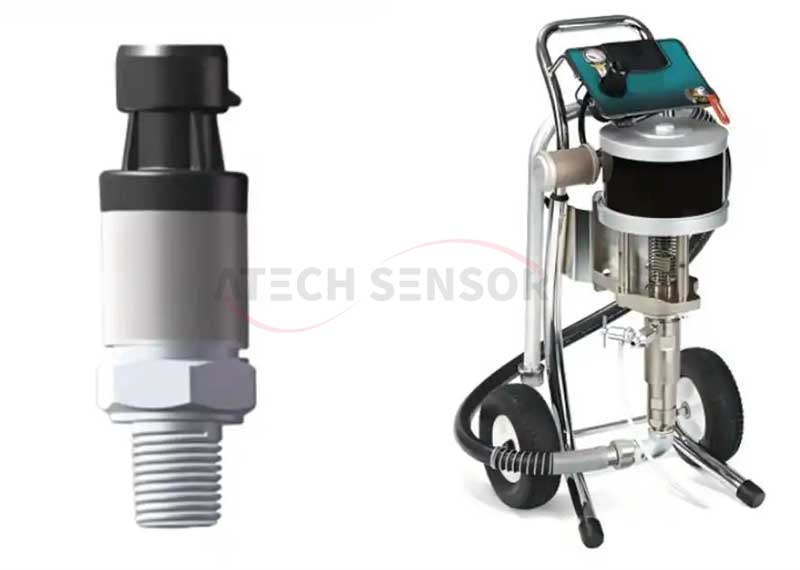
● Spraying equipment
In the airless spraying system, the paint can be evenly atomized. The pressure in the spraying material tank needs to be controlled in real time. The pressure sensor is installed on the top of the spraying material container to monitor the internal pressure of the spraying system.

● Glue injection system
In glue injection robot system, the flow rate/flow of glue is controlled according to pressure. The pressure sensor is used to detect the pressure in the glue injection system. The sensor is installed in the pressure pipeline, which is connected to the glue container. The control system monitors the pipeline pressure in real time and adjusts it in real time to ensure the stability of the system pressure. The sensor needs to be flush membrane, corrosion-resistant and small size.

● Injection Molding Machine
The injection unit is responsible for heating the material in the reciprocating screw barrel and distributing it into the mold cavity. Injection mold materials usually flow under high pressure, and if the injection pressure is incorrect, the material may cause defects in molded parts, damage to the mold, and machine downtime, among other effects.
● Hydraulic system
The pressure of the hydraulic system is the working power of all hydraulic actuators and the control center of most hydraulic control components. It is applied in hydraulic pipelines and can directly reflect the working status of the hydraulic system. It is the core of the entire system. The pressure sensor is a key component in the hydraulic system. It can cooperate with PLC to better meet the control accuracy requirements of the target pressure.

● Semiconductor Industry MFC
Gas mass flow controllers (MFC) for semiconductors can use pressure sensors to convert flow rates.
● Gas valve control
In the industrial production process, air pressure valves integrate precise pressure sensors to achieve fine control of air pressure in various industrial processes, thereby ensuring a high degree of accuracy and reliability in production operations.
2) Automobile field: In automobile manufacturing, pressure sensors are widely used in engine fuel injection control, brake system pressure monitoring, tire pressure monitoring, etc., providing guarantees for automobile safety, energy saving and comfort.
● Power system
In the efficient control of automobile power system, intake pressure sensor, as a key technology, is playing an important role. The intake pressure sensor can accurately measure the pressure of the engine intake duct and provide important data support for the engine control unit. It not only ensures the stable and efficient operation of the engine, but also provides a key foundation for the power output and fuel economy of the car.
● Braking system
The automotive brake pressure sensor can be used to control the oil pressure of the brake system with oil pressure booster. It can sensitively detect the pressure of the accumulator, the closing or disconnection signal of the output oil pump, and the abnormal alarm of oil pressure.

● Battery pack detection
Pressure sensors are usually installed at key locations inside the battery pack to ensure accurate monitoring of the gas pressure in the entire battery pack. It senses the changes in gas pressure in the battery pack and converts the pressure signal into an electrical signal output for real-time monitoring and processing by the monitoring system.
● Tire pressure detection
The tire pressure monitoring system is referred to as "TPMS". From January 1, 2020, all passenger cars in production will begin to implement the mandatory installation of TPMS (tire pressure monitoring system). TPMS, airbags, and ABS (anti-lock braking) systems constitute the three major safety systems of automobiles.
3) Medical field: In the medical field, pressure sensors are widely used in blood pressure measurement, ventilator pressure monitoring, hemodialysis pressure control, etc., providing important support for the precise control of medical equipment and patient safety.
● Blood pressure measurement
There are two types of blood pressure measurement: non-invasive and invasive. Common non-invasive blood pressure monitors include arm blood pressure monitors and desktop blood pressure monitors.

Invasive blood pressure measurement technology is usually used in ICUs (intensive care units), where dedicated pressure sensors are in direct contact with the patient's blood to ensure measurement accuracy. In order to meet medical safety and hygiene requirements, these pressure sensors are usually disposable to ensure sterility and patient safety for each measurement.
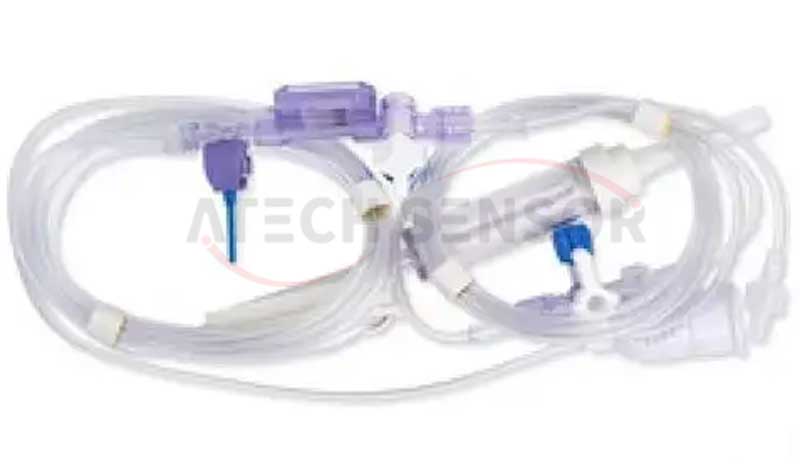
● Ventilator
Ventilator generally uses about 6 pressure sensors: 2 absolute pressure (or gauge pressure) pressure sensors for airway pressure measurement, 2 differential pressure pressure sensors for flow (flow velocity) measurement, 1 absolute pressure (gauge pressure) pressure sensor and 1 differential pressure pressure sensor for forming a self-test system, which is used to compare the pressure values of each airway pressure sensor and issue a fault alarm.
● Dialysis Machines
Pressure sensors in dialysis machines are essential for real-time blood pressure monitoring during all phases of treatment. Arterial sensors track the patient’s blood pressure while ensuring that red blood cells are protected from harm. Venous sensors, on the other hand, track the pressure of dialyzed blood returning to the patient’s body and help detect potential problems, such as blocked tubing.
● IVD blood analyzer
In IVD instruments, the pressure detected by the pressure sensor can be fed back to the control system to control the start and stop of pumps, valves and other devices. The pressure detected by the pressure sensor can also be fed back to the alarm system to alarm the working status of the system and the status of the device. This allows operators to accurately grasp the status of the instrument and engineers to accurately locate the problem.

4) Consumer sector: MEMS pressure sensors are increasingly used in the consumer electronics market, especially in devices such as smartphones and smart watches. These sensors can provide highly accurate pressure measurements for a variety of functions such as altitude measurement, weather forecasting, and indoor navigation.
● Smart wearable devices
Smart watches and health trackers are important application areas for MEMS pressure sensors. These devices use pressure sensors to monitor users' activity levels, heart rate, blood oxygen saturation and other physiological parameters.
● Smartphones and Tablets
MEMS pressure sensors are becoming more common in smartphones and tablets. These sensors are not only used for traditional air pressure measurement, but are also beginning to be used in emerging applications such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mobile payments.
● Drones
Pressure sensors detect the Earth's atmospheric pressure. The data provided by the barometer can help the drone navigate to the desired altitude and accurately estimate the ascent and descent speeds, which is very important for drone flight control.
The pitot tube or pitot tube on the aircraft is an important atmospheric data system sensor. The differential pressure sensor can be used to accurately import the static pressure and total pressure airflow of the surrounding atmosphere of the aircraft under flight conditions. These measurement data can be converted into flight parameters such as pressure altitude, indicated airspeed, and ascent and descent rate, and displayed and output on the instrument.

6. Precautions for using pressure sensors
Sensors are sensitive components. When using pressure sensors, you need to pay attention to the following points:
1) Choose the appropriate model and specification: Choose the appropriate pressure sensor model and specification according to the measurement requirements to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results.
Main parameters of pressure sensor:
● Range: micro pressure (below 1PSI), low pressure (below 100PSI), medium pressure (below 750PSI), high pressure (greater than 750PSI)
● Non-linearity Non-linearity unit: %FS
● Sensitivity
● Repeatability
● Zero drift
● Temperature compensation
● Annual drift
● Measurement type: absolute pressure, gauge pressure, differential pressure, mixed pressure.
2) Correct installation and use: Install and use the sensor correctly according to the requirements in the sensor manual to avoid measurement errors or sensor damage caused by improper installation or operating errors.
3) Regular maintenance and calibration: Regularly maintain and calibrate the sensor to ensure its long-term stable operation and measurement accuracy.
4) Pay attention to the influence of environmental factors: During use, pay attention to the influence of environmental factors on sensor performance, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, etc., and take appropriate measures to compensate or eliminate them.
7. Conclusion
If you have any selection requirements or purchasing intentions, please feel free to contact Xi'an Guanke. For more exciting sensor content, please follow Xi'an Guanke Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.

