Definition of temperature sensor
Temperature sensor, as the name implies, is a device that can sense the temperature of the object being measured and convert it into a measurable and transmittable signal. These signals are usually electrical signals (such as changes in voltage, current or resistance value) to facilitate subsequent processing, display or control. Temperature sensor realizes the conversion of non-electrical quantity (temperature) to electrical quantity through its unique sensitive element, and is an important bridge between modern information technology and industrial control.
Classification of temperature sensors
There are many types of temperature sensors, which can be roughly divided into the following categories according to the measurement principle, materials used, output signal form, etc.:
1. Thermistor temperature sensor: It uses the property that the resistance value of metal or semiconductor materials changes with temperature to measure temperature. Common thermistors include platinum thermistors (Pt100, Pt1000) and copper thermistors.
2. Thermocouple temperature sensor: It is based on the thermoelectric effect, that is, the principle that two conductors of different materials generate electromotive force at the junction due to temperature difference. Thermocouples have the characteristics of wide measurement range, good linearity, and high temperature resistance, and are often used for high temperature measurement.
3. Integrated temperature sensor: It integrates temperature sensitive elements and their signal processing circuits on the same chip. It has the advantages of small size, low power consumption, fast response, and high accuracy. It is widely used in portable electronic products.
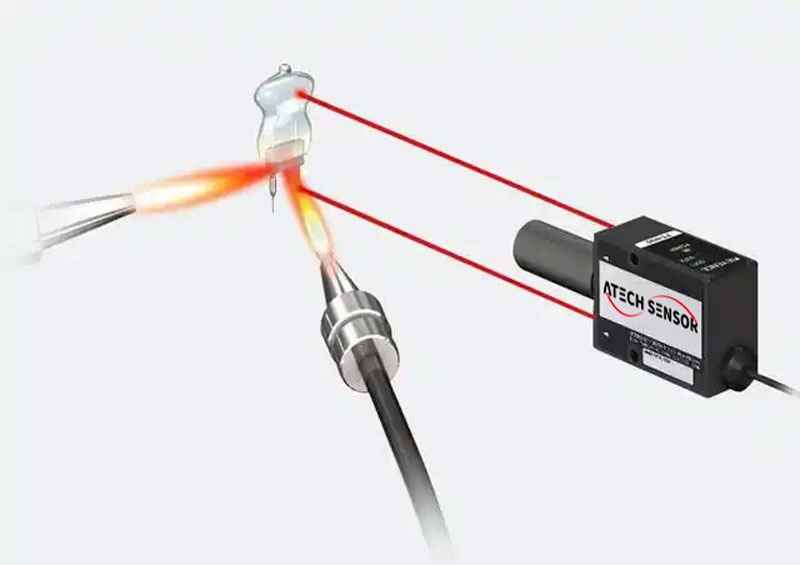
4. Infrared temperature sensor: It measures the infrared energy radiated from the surface of an object to infer its temperature. It is non-contact measurement and is suitable for fast and remote temperature measurement scenarios.
5. Semiconductor temperature sensor: It uses the temperature characteristics of semiconductor materials (such as PN junctions) to measure temperature, including thermistors, thermal diodes, etc., which have the characteristics of high sensitivity and low cost.
Working Principle of Temperature Sensor
Taking the most commonly used thermal resistor temperature sensor as an example, its working principle is based on the characteristic that the resistivity of metal materials changes with temperature. When the temperature changes, the microscopic parameters of the metal material such as electron mobility and lattice vibration change, causing the resistivity to change accordingly. For platinum thermal resistor (Pt100), its resistance value is 100Ω at 0℃, and as the temperature rises, the resistance value increases approximately linearly. By measuring the change in resistance value and combining it with the known resistance-temperature relationship curve, the temperature of the object being measured can be inferred.
The working principle of thermocouple is based on the thermoelectric effect, that is, when two conductors A and B of different materials form a closed loop, if there is a temperature difference ΔT at the two junctions, an electromotive force E will be generated in the loop. The electromotive force is proportional to the temperature difference and is related to the conductor material and the loop structure. By measuring the size of the electromotive force and combining it with the thermocouple graduation table, the temperature value can be determined.

4. The important role of temperature sensors in practical applications
1. Industrial control: In the steel, chemical, electric power and other industries, temperature sensors are used to monitor equipment temperature, prevent equipment damage or safety accidents caused by overheating, and ensure production safety.
2. Environmental monitoring: In meteorological observation, greenhouse planting and other fields, temperature sensors help monitor environmental temperature and provide important data support for agricultural production and climate research.
3. Smart home: In smart air conditioners, refrigerators and other home appliances, temperature sensors can automatically adjust the temperature, improve living comfort, and save energy and reduce emissions.
4. Medical equipment: In thermometers, constant temperature incubators and other equipment, temperature sensors ensure accurate temperature control during the medical process, ensuring patient safety and treatment effects.
5. Scientific research experiments: In laboratories, high-precision temperature sensors are used in various physical, chemical and biological experiments to ensure accurate control of experimental conditions and improve the reliability of experimental results.

